4.4 nn.BatchNorm2d用法详解
joker ... 2022-4-7 大约 3 分钟
# 4.4 nn.BatchNorm2d用法详解
# 简介
BatchNorm2d()函数数学原理如下:
代码
torch.nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True,
track_running_stats=True, device=None, dtype=None)
1
2
2
参数详解
num_features:指特征数。 一般情况下输入的数据格式为(batch_size ,num_features , height , width)其中的C为特征数,也称channel数eps:为分数值稳定而添加到分母的值。 默认值:1e-5momentum:一个用于运行过程中均值和方差的一个估计参数。 可以将累积移动平均线(即简单平均线)设置为None。 默认值:0.1affine:一个布尔值,当设置为True时,此模块具有可学习的仿射参数。γ(gamma) 和 β(beta) (可学习的仿射变换参数) 默认值:Truetrack_running_stats:一个布尔值,当设置为True时,此模块跟踪运行平均值和方差;设置为False时,此模块不跟踪此类统计信息,并将统计信息缓冲区running_mean和running_var初始化为None。 当这些缓冲区为None时,此模块将始终使用批处理统计信息。 在训练和评估模式下都可以。 默认值:True
# 作用
机器学习中,进行模型训练之前,需对数据做归一化处理,使其分布一致。在深度神经网络训练过程中,通常一次训练是一个batch,而非全体数据。每个batch具有不同的分布产生了internal covarivate shift问题——在训练过程中,数据分布会发生变化,对下一层网络的学习带来困难。Batch Normalization强行将数据拉回到均值为0,方差为1的正太分布上,一方面使得数据分布一致,另一方面避免梯度消失。
# 运算
说明Batch Normalization的原理。假设在网络中间经过某些卷积操作之后的输出的feature maps的尺寸为N×C×W×H,5为batch size(N),3为channel(C),W×H为feature map的宽高,则Batch Normalization的计算过程如下:
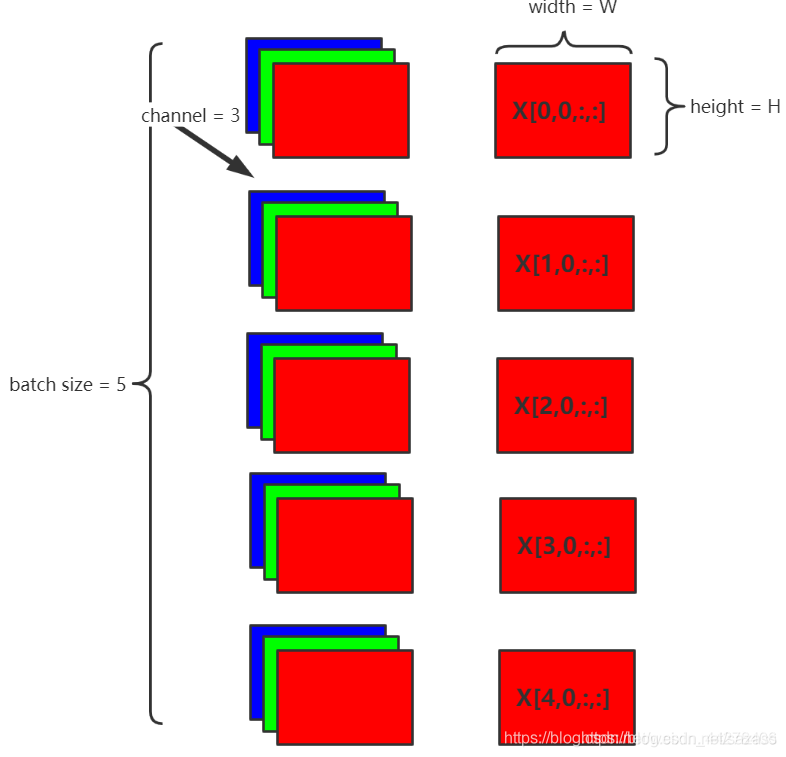
每个batch计算同一通道的均值,如图取channel 0,即(红色表示)
每个batch计算同一通道的方差
对当前channel下feature map中每个点,索引形式,做归一化
增加缩放和平移变量 γ 和 β (可学习的仿射变换参数),归一化后的值
简化公式
# 代码
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
def checkBN(debug = False):
# parameters
N = 5 # batch size
C = 3 # channel
W = 2 # width of feature map
H = 2 # height of feature map
# batch normalization layer
BN = nn.BatchNorm2d(C,affine=True) #gamma和beta, 其维度与channel数相同
# input and output
featuremaps = torch.randn(N,C,W,H)
output = BN(featuremaps)
# checkout
###########################################
if debug:
print("input feature maps:\n",featuremaps)
print("normalized feature maps: \n",output)
###########################################
# manually operation, the first channel
X = featuremaps[:,0,:,:]
firstDimenMean = torch.Tensor.mean(X)
firstDimenVar = torch.Tensor.var(X,False) #Bessel's Correction贝塞尔校正不被使用
BN_one = ((input[0,0,0,0] - firstDimenMean)/(torch.pow(firstDimenVar+BN.eps,0.5) )) * BN.weight[0] + BN.bias[0]
print('+++'*15,'\n','manually operation: ', BN_one)
print('==='*15,'\n','pytorch result: ', output[0,0,0,0])
if __name__=="__main__":
checkBN()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
可以看出手算的结果和PyTorch的nn.BatchNorm2d的计算结果一致:
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
manually operation: tensor(-0.0327, grad_fn=<AddBackward0>)
=============================================
pytorch result: tensor(-0.0327, grad_fn=<SelectBackward>)
1
2
3
4
2
3
4
官方演示代码
>>> # With Learnable Parameters
>>> m = nn.BatchNorm2d(100)
>>> # Without Learnable Parameters
>>> m = nn.BatchNorm2d(100, affine=False)
>>> input = torch.randn(20, 100, 35, 45)
>>> output = m(input)
1
2
3
4
5
6
2
3
4
5
6